Add user to sudoers file, list or group so that you can give a new user root access or privilege. How do I add a user to Sudoers? How do I give a user Sudo permission? How do I edit Sudoers? How do I add a user to Sudoers Visudo? Believe it or not, these are fairly common questions and in all reality the answer is quite simple.
Adding a user on a fully installed Debian or Ubuntu Linux based system is possible by issuing the visudo command. Users in the sudoer group are allowed privileges to run commands and open files as root or administrator. The following segment covers the simple process of adding a new root user to Debian or Ubuntu based systems.
Note: Ubuntu and Debian Live distributions come with no root password by default. So, if your running from a Live distro, you will likely need to set a Debian or Ubuntu default root password before proceeding.
How do I set a root password for Linux?
To set a root password for Linux,
- Open a terminal Ctrl + Alt + T
- Type the following command and then press Enter
sudo passwd root
All of the sections that follow assume that your system has the root account enabled and a password has been set for root.
How to add user to Sudoers Debian
To add a user to sudoers file for Debian based systems,
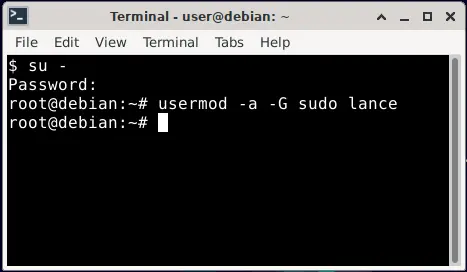
- Open a terminal Ctrl + Alt + T
- Type the following and press Enter to change to superuser.
su -
Then type your root password when prompted.
- Next, (replacing username with the actual user you want to add), type the following and press Enter.
usermod -a -G sudo username
How to fix bash: sudo: command not found
If you get an error stating "bash: sudo: command not found", you can fix it by typing apt -y install sudo after becoming superuser in step 2.
That's all there is to it. You can now switch back to the user you added by issuing the following command,
sudo su username
and then test that the user has root privileges by trying to run a sudo command like
sudo apt update
How to add user to Sudoers Ubuntu
The following covers the process of adding a new root user (sudoer) to an Ubuntu or Debian based system. Here we are using the visudo command to open the sudoers file for editing. We then proceed to add a user to give root access and grant sudo privileges to.
- Open a new terminal Ctrl + Alt + T
- Type the following and then press Enter (to change to root user).
sudo su
- Next, type thew following and press Enter (to access and edit the list).
visudo
- Using the up/down arrows, navigate to the bottom of the sudoers file.
- Add the following line at the end of the sudoers list, replacing "username" with the actual username:
username ALL=(ALL) ALL
- Finally, press Ctrl+X and then press y when prompted to save and close the file.
Note: Be careful when editing the sudoers file, as a mistake can prevent you from being able to use sudo.
New Sudoer user added to group with root access
If all went well, your sudoers file should look similar to the one shown below. The added user should now be able to use the sudo command to run commands as the root user.
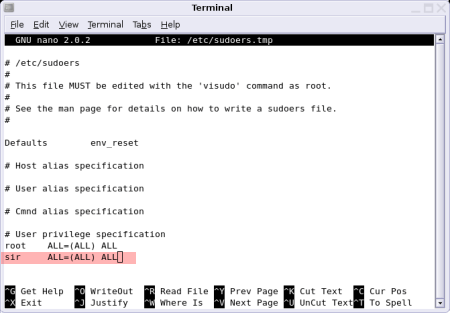
That is really all it takes to do this from a Debian or Ubuntu based operating environment. Keep in mind that you can repeat the process, (adding a new line) for as many users as you would like to add. Visudo might also come in handy for those times when you need to remove existing root users from the sudoers file. So you can use visudo to delete and grant sudo privileges, on the fly.
How to add user to Sudoers Centos
To add a new sudo user, (adding them to the "wheel" group) in CentOS 7 or 8, follow these steps:
Note: The wheel group is the default group in CentOS that has sudo privileges.
- Open a terminal.
- Type the following command and press enter (to login as root).
su -
- Type the following, replacing "username" with the actual username, (to add the new user to the sudo group):
usermod -aG wheel username
Testing the new user add to wheel group
To test that the new user was successfully added to the wheel group or sudo group in CentOS, simply perform the following commands from an open terminal, replacing "username" with the actual username.
Type
su - username
and then see if the user has sudo privileges with,
sudo whoami
This concludes the procedure to add user to sudoers file from Debian or Ubuntu, or add to wheel group from CentOS Linux. I'll provide a follow-up at a later point in time with a process to grant sudo privileges to users for Arch, and other Linux operating systems.